Como fazer uma IA de um cervo no Unity
No desenvolvimento do jogo, adicionar Inteligência Artificial significa escrever código que controlará a entidade do jogo sem qualquer entrada externa.
Animal AI in games é um ramo da AI que visa traduzir o comportamento animal no ambiente digital do jogo para criar uma experiência realista.
Neste tutorial, mostrarei como fazer um animal simples (Deer) AI em Unity que terá dois estados , ocioso e fugir.
Etapa 1: Prepare a Cena e o Modelo do Cervo
Precisaremos de um nível e um modelo de veado.
Para o nível, usarei um terreno simples com um pouco de grama e árvores:
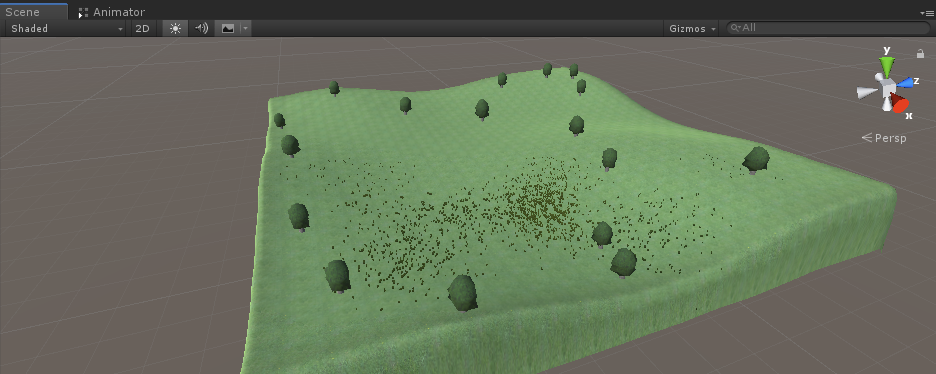
Para o modelo Cervo eu simplesmente combinei alguns Cubos (mas você pode usar este modelo cervo):

Agora vamos para a parte de codificação.
Etapa 2: configurar o Player Controller
Começamos configurando um Player Controller para que possamos andar por aí e testar a IA:
- Crie um novo script, nomeie-o SC_CharacterController e cole o código abaixo dentro dele:
SC_CharacterController.cs
using UnityEngine;
[RequireComponent(typeof(CharacterController))]
public class SC_CharacterController : MonoBehaviour
{
public float speed = 7.5f;
public float jumpSpeed = 8.0f;
public float gravity = 20.0f;
public Camera playerCamera;
public float lookSpeed = 2.0f;
public float lookXLimit = 45.0f;
CharacterController characterController;
Vector3 moveDirection = Vector3.zero;
Vector2 rotation = Vector2.zero;
[HideInInspector]
public bool canMove = true;
void Start()
{
characterController = GetComponent<CharacterController>();
rotation.y = transform.eulerAngles.y;
}
void Update()
{
if (characterController.isGrounded)
{
// We are grounded, so recalculate move direction based on axes
Vector3 forward = transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.forward);
Vector3 right = transform.TransformDirection(Vector3.right);
float curSpeedX = speed * Input.GetAxis("Vertical");
float curSpeedY = speed * Input.GetAxis("Horizontal");
moveDirection = (forward * curSpeedX) + (right * curSpeedY);
if (Input.GetButton("Jump"))
{
moveDirection.y = jumpSpeed;
}
}
// Apply gravity. Gravity is multiplied by deltaTime twice (once here, and once below
// when the moveDirection is multiplied by deltaTime). This is because gravity should be applied
// as an acceleration (ms^-2)
moveDirection.y -= gravity * Time.deltaTime;
// Move the controller
characterController.Move(moveDirection * Time.deltaTime);
// Player and Camera rotation
if (canMove)
{
rotation.y += Input.GetAxis("Mouse X") * lookSpeed;
rotation.x += -Input.GetAxis("Mouse Y") * lookSpeed;
rotation.x = Mathf.Clamp(rotation.x, -lookXLimit, lookXLimit);
playerCamera.transform.localRotation = Quaternion.Euler(rotation.x, 0, 0);
transform.eulerAngles = new Vector2(0, rotation.y);
}
}
}![]()
- Crie um novo GameObject e nomeie-o como "Player" e altere sua tag para "Player"
- Crie uma nova Cápsula (GameObject -> Objeto 3D -> Cápsula), então torne-a um objeto filho do Objeto "Player", mude sua posição para (0, 1, 0) , e remova seu componente CapsuleCollider.
- Mova a câmera principal dentro do objeto "Player" e mude sua posição para (0, 1.64, 0)
- Anexar script SC_CharacterController a um objeto "Player" (Você notará que ele também adicionará outro componente chamado Character Controller. Defina seu valor central para (0, 1, 0))
- Atribua a câmera principal à variável "Player Camera" em SC_CharacterController e salve a cena
O Player Controller está pronto.
Etapa 3: Programe Deer AI
Agora vamos para a parte onde programamos uma Deer AI:
- Crie um novo script e nomeie-o SC_DeerAI (este script controlará o movimento da IA):
![]()
Abra SC_DeerAI e continue as etapas abaixo:
No início do script, garantimos que todas as classes necessárias foram incluídas (especificamente UnityEngine.AI):
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.AI;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class SC_DeerAI : MonoBehaviour
{Agora vamos somar todas as variáveis:
public enum AIState { Idle, Walking, Eating, Running }
public AIState currentState = AIState.Idle;
public int awarenessArea = 15; //How far the deer should detect the enemy
public float walkingSpeed = 3.5f;
public float runningSpeed = 7f;
public Animator animator;
//Trigger collider that represents the awareness area
SphereCollider c;
//NavMesh Agent
NavMeshAgent agent;
bool switchAction = false;
float actionTimer = 0; //Timer duration till the next action
Transform enemy;
float range = 20; //How far the Deer have to run to resume the usual activities
float multiplier = 1;
bool reverseFlee = false; //In case the AI is stuck, send it to one of the original Idle points
//Detect NavMesh edges to detect whether the AI is stuck
Vector3 closestEdge;
float distanceToEdge;
float distance; //Squared distance to the enemy
//How long the AI has been near the edge of NavMesh, if too long, send it to one of the random previousIdlePoints
float timeStuck = 0;
//Store previous idle points for reference
List<Vector3> previousIdlePoints = new List<Vector3>(); Então inicializamos tudo no void Start():
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
agent = GetComponent<NavMeshAgent>();
agent.stoppingDistance = 0;
agent.autoBraking = true;
c = gameObject.AddComponent<SphereCollider>();
c.isTrigger = true;
c.radius = awarenessArea;
//Initialize the AI state
currentState = AIState.Idle;
actionTimer = Random.Range(0.1f, 2.0f);
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}(Como você pode ver, adicionamos um Sphere Collider que está marcado como Trigger. Este colisor atuará como uma área de reconhecimento quando o inimigo entrar nele).
A lógica AI real é feita no void Update() com algumas funções auxiliares:
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
//Wait for the next course of action
if (actionTimer > 0)
{
actionTimer -= Time.deltaTime;
}
else
{
switchAction = true;
}
if (currentState == AIState.Idle)
{
if(switchAction)
{
if (enemy)
{
//Run away
agent.SetDestination(RandomNavSphere(transform.position, Random.Range(1, 2.4f)));
currentState = AIState.Running;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
else
{
//No enemies nearby, start eating
actionTimer = Random.Range(14, 22);
currentState = AIState.Eating;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
//Keep last 5 Idle positions for future reference
previousIdlePoints.Add(transform.position);
if (previousIdlePoints.Count > 5)
{
previousIdlePoints.RemoveAt(0);
}
}
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Walking)
{
//Set NavMesh Agent Speed
agent.speed = walkingSpeed;
// Check if we've reached the destination
if (DoneReachingDestination())
{
currentState = AIState.Idle;
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Eating)
{
if (switchAction)
{
//Wait for current animation to finish playing
if(!animator || animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0).normalizedTime - Mathf.Floor(animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0).normalizedTime) > 0.99f)
{
//Walk to another random destination
agent.destination = RandomNavSphere(transform.position, Random.Range(3, 7));
currentState = AIState.Walking;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Running)
{
//Set NavMesh Agent Speed
agent.speed = runningSpeed;
//Run away
if (enemy)
{
if (reverseFlee)
{
if (DoneReachingDestination() && timeStuck < 0)
{
reverseFlee = false;
}
else
{
timeStuck -= Time.deltaTime;
}
}
else
{
Vector3 runTo = transform.position + ((transform.position - enemy.position) * multiplier);
distance = (transform.position - enemy.position).sqrMagnitude;
//Find the closest NavMesh edge
NavMeshHit hit;
if (NavMesh.FindClosestEdge(transform.position, out hit, NavMesh.AllAreas))
{
closestEdge = hit.position;
distanceToEdge = hit.distance;
//Debug.DrawLine(transform.position, closestEdge, Color.red);
}
if (distanceToEdge < 1f)
{
if(timeStuck > 1.5f)
{
if(previousIdlePoints.Count > 0)
{
runTo = previousIdlePoints[Random.Range(0, previousIdlePoints.Count - 1)];
reverseFlee = true;
}
}
else
{
timeStuck += Time.deltaTime;
}
}
if (distance < range * range)
{
agent.SetDestination(runTo);
}
else
{
enemy = null;
}
}
//Temporarily switch to Idle if the Agent stopped
if(agent.velocity.sqrMagnitude < 0.1f * 0.1f)
{
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Idle);
}
else
{
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Running);
}
}
else
{
//Check if we've reached the destination then stop running
if (DoneReachingDestination())
{
actionTimer = Random.Range(1.4f, 3.4f);
currentState = AIState.Eating;
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Idle);
}
}
}
switchAction = false;
}
bool DoneReachingDestination()
{
if (!agent.pathPending)
{
if (agent.remainingDistance <= agent.stoppingDistance)
{
if (!agent.hasPath || agent.velocity.sqrMagnitude == 0f)
{
//Done reaching the Destination
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void SwitchAnimationState(AIState state)
{
//Animation control
if (animator)
{
animator.SetBool("isEating", state == AIState.Eating);
animator.SetBool("isRunning", state == AIState.Running);
animator.SetBool("isWalking", state == AIState.Walking);
}
}
Vector3 RandomNavSphere(Vector3 origin, float distance)
{
Vector3 randomDirection = Random.insideUnitSphere * distance;
randomDirection += origin;
NavMeshHit navHit;
NavMesh.SamplePosition(randomDirection, out navHit, distance, NavMesh.AllAreas);
return navHit.position;
}(Cada Estado inicializa os valores e o alvo do Agente NavMesh para o próximo estado. Por exemplo, o estado Ocioso tem 2 resultados possíveis, ele inicializa o estado Correndo se o inimigo estiver presente ou o estado Comendo se nenhum inimigo cruzou a área de reconhecimento.
Um estado de caminhada é usado entre os estados de Comer para se mover para o novo destino.
O estado de corrida calcula a direção relativa à posição do inimigo, para correr diretamente dela.
Se ficar preso no canto, o AI se retrai para uma das posições ociosas salvas anteriormente. O inimigo está perdido depois que a IA está longe o suficiente do inimigo).
E, finalmente, adicionamos um evento OnTriggerEnter que monitorará o Colisor de Esferas (também conhecido como Área de Conscientização) e inicializará o estado de Corrida assim que o inimigo chegar muito perto:
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
//Make sure the Player instance has a tag "Player"
if (!other.CompareTag("Player"))
return;
enemy = other.transform;
actionTimer = Random.Range(0.24f, 0.8f);
currentState = AIState.Idle;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}Assim que o jogador entra no gatilho, a variável inimigo é atribuída e o estado Idle é inicializado, depois disso, o estado Running é inicializado.
Abaixo está o script SC_DeerAI.cs final:
//You are free to use this script in Free or Commercial projects
//sharpcoderblog.com @2019
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.AI;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class SC_DeerAI : MonoBehaviour
{
public enum AIState { Idle, Walking, Eating, Running }
public AIState currentState = AIState.Idle;
public int awarenessArea = 15; //How far the deer should detect the enemy
public float walkingSpeed = 3.5f;
public float runningSpeed = 7f;
public Animator animator;
//Trigger collider that represents the awareness area
SphereCollider c;
//NavMesh Agent
NavMeshAgent agent;
bool switchAction = false;
float actionTimer = 0; //Timer duration till the next action
Transform enemy;
float range = 20; //How far the Deer have to run to resume the usual activities
float multiplier = 1;
bool reverseFlee = false; //In case the AI is stuck, send it to one of the original Idle points
//Detect NavMesh edges to detect whether the AI is stuck
Vector3 closestEdge;
float distanceToEdge;
float distance; //Squared distance to the enemy
//How long the AI has been near the edge of NavMesh, if too long, send it to one of the random previousIdlePoints
float timeStuck = 0;
//Store previous idle points for reference
List<Vector3> previousIdlePoints = new List<Vector3>();
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
agent = GetComponent<NavMeshAgent>();
agent.stoppingDistance = 0;
agent.autoBraking = true;
c = gameObject.AddComponent<SphereCollider>();
c.isTrigger = true;
c.radius = awarenessArea;
//Initialize the AI state
currentState = AIState.Idle;
actionTimer = Random.Range(0.1f, 2.0f);
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
//Wait for the next course of action
if (actionTimer > 0)
{
actionTimer -= Time.deltaTime;
}
else
{
switchAction = true;
}
if (currentState == AIState.Idle)
{
if(switchAction)
{
if (enemy)
{
//Run away
agent.SetDestination(RandomNavSphere(transform.position, Random.Range(1, 2.4f)));
currentState = AIState.Running;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
else
{
//No enemies nearby, start eating
actionTimer = Random.Range(14, 22);
currentState = AIState.Eating;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
//Keep last 5 Idle positions for future reference
previousIdlePoints.Add(transform.position);
if (previousIdlePoints.Count > 5)
{
previousIdlePoints.RemoveAt(0);
}
}
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Walking)
{
//Set NavMesh Agent Speed
agent.speed = walkingSpeed;
// Check if we've reached the destination
if (DoneReachingDestination())
{
currentState = AIState.Idle;
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Eating)
{
if (switchAction)
{
//Wait for current animation to finish playing
if(!animator || animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0).normalizedTime - Mathf.Floor(animator.GetCurrentAnimatorStateInfo(0).normalizedTime) > 0.99f)
{
//Walk to another random destination
agent.destination = RandomNavSphere(transform.position, Random.Range(3, 7));
currentState = AIState.Walking;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
}
}
else if (currentState == AIState.Running)
{
//Set NavMesh Agent Speed
agent.speed = runningSpeed;
//Run away
if (enemy)
{
if (reverseFlee)
{
if (DoneReachingDestination() && timeStuck < 0)
{
reverseFlee = false;
}
else
{
timeStuck -= Time.deltaTime;
}
}
else
{
Vector3 runTo = transform.position + ((transform.position - enemy.position) * multiplier);
distance = (transform.position - enemy.position).sqrMagnitude;
//Find the closest NavMesh edge
NavMeshHit hit;
if (NavMesh.FindClosestEdge(transform.position, out hit, NavMesh.AllAreas))
{
closestEdge = hit.position;
distanceToEdge = hit.distance;
//Debug.DrawLine(transform.position, closestEdge, Color.red);
}
if (distanceToEdge < 1f)
{
if(timeStuck > 1.5f)
{
if(previousIdlePoints.Count > 0)
{
runTo = previousIdlePoints[Random.Range(0, previousIdlePoints.Count - 1)];
reverseFlee = true;
}
}
else
{
timeStuck += Time.deltaTime;
}
}
if (distance < range * range)
{
agent.SetDestination(runTo);
}
else
{
enemy = null;
}
}
//Temporarily switch to Idle if the Agent stopped
if(agent.velocity.sqrMagnitude < 0.1f * 0.1f)
{
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Idle);
}
else
{
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Running);
}
}
else
{
//Check if we've reached the destination then stop running
if (DoneReachingDestination())
{
actionTimer = Random.Range(1.4f, 3.4f);
currentState = AIState.Eating;
SwitchAnimationState(AIState.Idle);
}
}
}
switchAction = false;
}
bool DoneReachingDestination()
{
if (!agent.pathPending)
{
if (agent.remainingDistance <= agent.stoppingDistance)
{
if (!agent.hasPath || agent.velocity.sqrMagnitude == 0f)
{
//Done reaching the Destination
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void SwitchAnimationState(AIState state)
{
//Animation control
if (animator)
{
animator.SetBool("isEating", state == AIState.Eating);
animator.SetBool("isRunning", state == AIState.Running);
animator.SetBool("isWalking", state == AIState.Walking);
}
}
Vector3 RandomNavSphere(Vector3 origin, float distance)
{
Vector3 randomDirection = Random.insideUnitSphere * distance;
randomDirection += origin;
NavMeshHit navHit;
NavMesh.SamplePosition(randomDirection, out navHit, distance, NavMesh.AllAreas);
return navHit.position;
}
void OnTriggerEnter(Collider other)
{
//Make sure the Player instance has a tag "Player"
if (!other.CompareTag("Player"))
return;
enemy = other.transform;
actionTimer = Random.Range(0.24f, 0.8f);
currentState = AIState.Idle;
SwitchAnimationState(currentState);
}
}- Coloque o Deer model na cena e anexe um NavMesh Agent, script SC_DeerAI , e o componente Animator a ele:

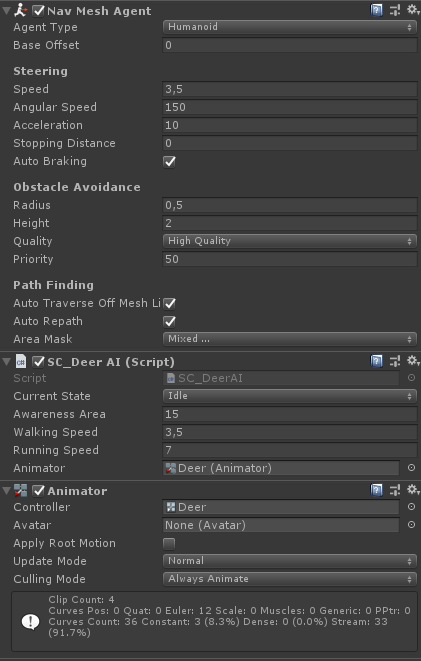
SC_DeerAI só tem uma variável que precisa ser atribuída, que é "Animator".
O componente animador requer um Controlador com 4 animações: Animação ociosa, Animação caminhando, Animação comendo e Animação correndo, e 3 parâmetros booleanos: isEating, isRunning e isWalking:
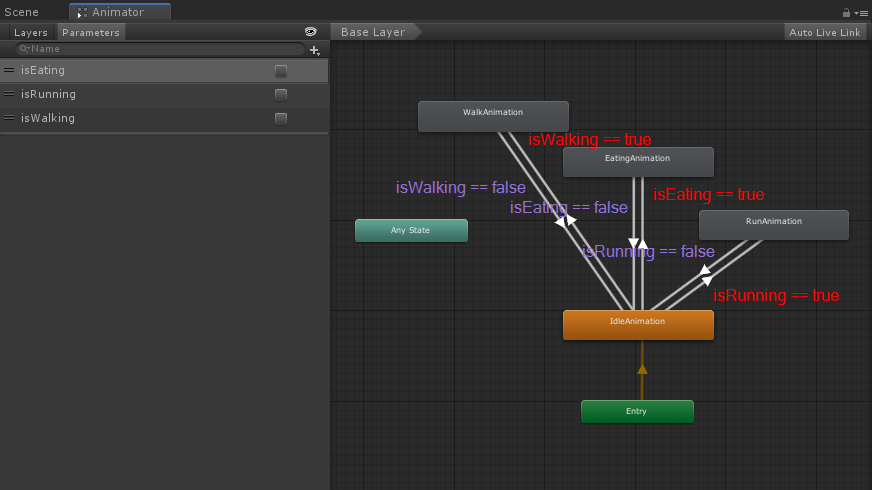
Você pode aprender como configurar um simples Animator Controller clicando em aqui
Depois de tudo atribuído, resta uma última coisa a fazer, que é criar um NavMesh.
- Selecione todos os Objetos de Cena que serão estáticos (Ex. Terreno, Árvores, etc.) e marque-os como "Navigation Static":
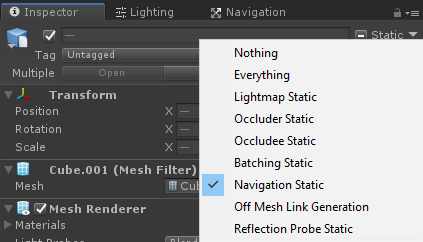
- Vá para a janela de navegação (Janela -> AI -> Navegação) e clique na guia "Bake" e, em seguida, clique no botão "Bake". Depois que o NavMesh estiver pronto, ele deve ficar mais ou menos assim:
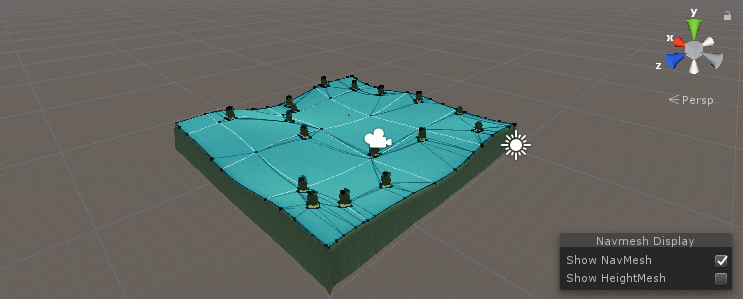
Depois que o NavMesh estiver pronto, podemos testar a IA:

Tudo funciona como esperado. O Cervo foge quando o inimigo está próximo e retoma suas atividades normais quando o inimigo está longe o suficiente.