Sincronizar corpos rígidos pela rede usando PUN 2
Sincronizar objetos no PUN 2 é simples, mas e quanto à sincronização de corpos rígidos?
Ao contrário dos GameObjects comuns, Rigidbody também é afetado pela Gravidade (se não pela Cinemática) e outros objetos também. Portanto, em vez de sincronizar apenas o Transform do objeto, também precisamos sincronizar alguns parâmetros adicionais, como velocity e angularVelocity.
Nesta postagem, mostrarei como criar corpos rígidos interativos que podem ser afetados por todos os jogadores na sala e sincronizados pela rede.
Unity versão usada neste tutorial: Unity 2018.3.0f2 (64 bits)
Parte 1: Configurando o PUN 2 e exemplo de multijogador
Já temos um tutorial de como configurar um exemplo multiplayer usando PUN 2, confira o link abaixo:
Faça um jogo multiplayer em Unity 3D usando PUN 2
Volte assim que terminar de configurar um projeto multijogador para que possamos continuar.
Como alternativa, você pode economizar tempo obtendo o projeto de origem aqui.
Parte 2: adicionando corpos rígidos interativos
Se você seguiu o tutorial acima, agora você teria 2 Cenas "GameLobby" e "GameLevel"
- Abra a cena "GameLevel" e crie alguns cubos (GameObject -> 3D Object -> Cube)
- Adicione um componente Rigidbody a cada cubo
- Adicione um componente PhotonView a cada cubo
Agora precisamos criar um novo Script que sincronizará os Rigidbodies pela rede.
- Crie um novo Script e chame-o de PUN2_RigidbodySync
PUN2_RigidbodySync.cs
using UnityEngine;
using Photon.Pun;
public class PUN2_RigidbodySync : MonoBehaviourPun, IPunObservable
{
Rigidbody r;
Vector3 latestPos;
Quaternion latestRot;
Vector3 velocity;
Vector3 angularVelocity;
bool valuesReceived = false;
// Start is called before the first frame update
void Start()
{
r = GetComponent<Rigidbody>();
}
public void OnPhotonSerializeView(PhotonStream stream, PhotonMessageInfo info)
{
if (stream.IsWriting)
{
//We own this player: send the others our data
stream.SendNext(transform.position);
stream.SendNext(transform.rotation);
stream.SendNext(r.velocity);
stream.SendNext(r.angularVelocity);
}
else
{
//Network player, receive data
latestPos = (Vector3)stream.ReceiveNext();
latestRot = (Quaternion)stream.ReceiveNext();
velocity = (Vector3)stream.ReceiveNext();
angularVelocity = (Vector3)stream.ReceiveNext();
valuesReceived = true;
}
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
if (!photonView.IsMine && valuesReceived)
{
//Update Object position and Rigidbody parameters
transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(transform.position, latestPos, Time.deltaTime * 5);
transform.rotation = Quaternion.Lerp(transform.rotation, latestRot, Time.deltaTime * 5);
r.velocity = velocity;
r.angularVelocity = angularVelocity;
}
}
void OnCollisionEnter(Collision contact)
{
if (!photonView.IsMine)
{
Transform collisionObjectRoot = contact.transform.root;
if (collisionObjectRoot.CompareTag("Player"))
{
//Transfer PhotonView of Rigidbody to our local player
photonView.TransferOwnership(PhotonNetwork.LocalPlayer);
}
}
}
}- Anexar PUN2_RigidbodySync a ambos os cubos e também atribuí-lo a Photon View "Observed Components":
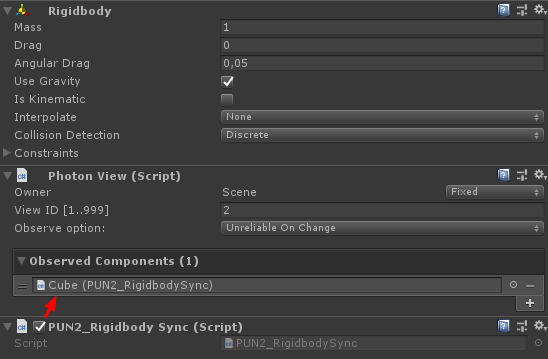
Também precisamos fazer algumas alterações no script PUN2_PlayerSync do tutorial Multijogador:
- Abra PUN2_PlayerSync.cs
- Em void Start(), dentro de if(photonView.IsMine) adicione este código:
//Player is local
gameObject.tag = "Player";
//Add Rigidbody to make the player interact with rigidbody
Rigidbody r = gameObject.AddComponent<Rigidbody>();
r.isKinematic = true;Então agora void Start() deve ficar assim:
// Use this for initialization
void Start()
{
if (photonView.IsMine)
{
//Player is local
gameObject.tag = "Player";
//Add Rigidbody to make the player interact with rigidbody
Rigidbody r = gameObject.AddComponent<Rigidbody>();
r.isKinematic = true;
}
else
{
//Player is Remote, deactivate the scripts and object that should only be enabled for the local player
for (int i = 0; i < localScripts.Length; i++)
{
localScripts[i].enabled = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < localObjects.Length; i++)
{
localObjects[i].SetActive(false);
}
}
}Ao adicionar um componente Rigidbody, garantimos que a instância do player possa interagir com outros Rigidbodies e, ao alterar a tag para "Player", podemos detectar se foi uma instância local que colidiu com um Rigidbody.
- Salve a cena GameLevel depois que tudo estiver pronto.
Agora vamos criar e testar!
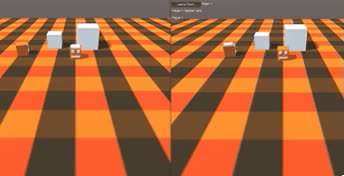
Tudo funciona como esperado, agora os Rigidbodies podem ser sincronizados pela rede enquanto ainda podem interagir.